If such a growth appears on a person's skin, he asks what changes have taken place in his body and whether it is dangerous. Read on for useful information on the characteristics of different types of papillomas. This information will help to identify the presence of such compounds in order to treat them in a timely manner, if necessary.
Types of papillomas
Why do these processes often appear on the skin with age? These changes in the skin are caused by human papillomavirus, or HPV for short. After infection with such a pathogen, the patient develops papillomatosis, during which warts of various shapes appear on the skin or mucous membranes. These growths are benign, but some papillomas have a high risk of recurrence as a malignant tumor. Therefore, if you see such changes in your skin, you must consult a doctor!
Medicine knows more than 40 types of papillomavirus that cause various forms of the disease in humans. The type of virus that enters the body depends on what the papilloma looks like, because the infection manifests itself in different formations in different parts of the body. According to the general classification, the following types of growth differ.
- Dark-colored keratinized growths are also called simple.
- Plantar - affects the heel.
- Accordions are rope-like formations with a body resting on one leg.
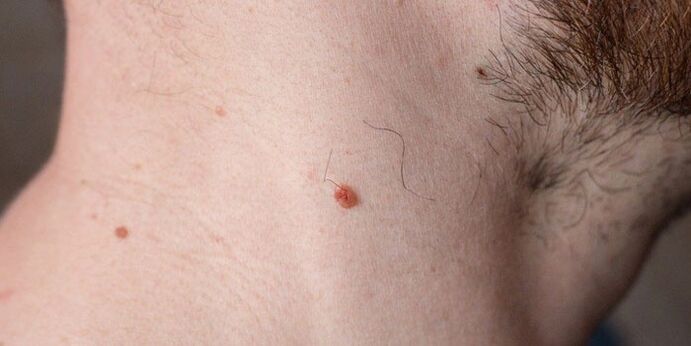
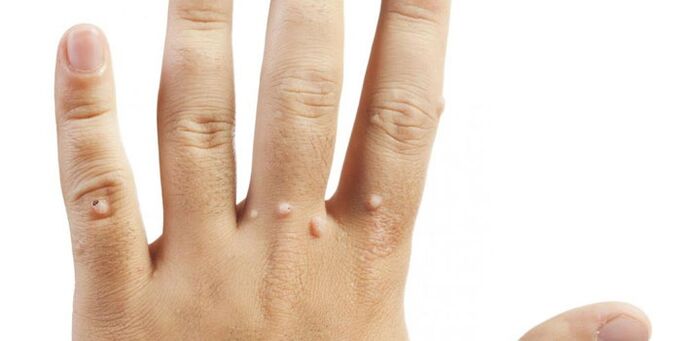
- Straight forms or common warts - often occur in adolescents with hands, fingers, facial area.
- Sharp - localized in the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, genitals or anus.
- Squamous cells are composed of squamous epithelium and stroma (the basis of connective tissue and blood vessels) that grow under the influence of the virus.
- Basal cell - formed from cells of the basal layer of the epidermis or hair follicles.
- Internal - occurs not in the region of the visible parts of the body, but in places where it is difficult to distinguish, for example, in the larynx or bladder.
He pointed out
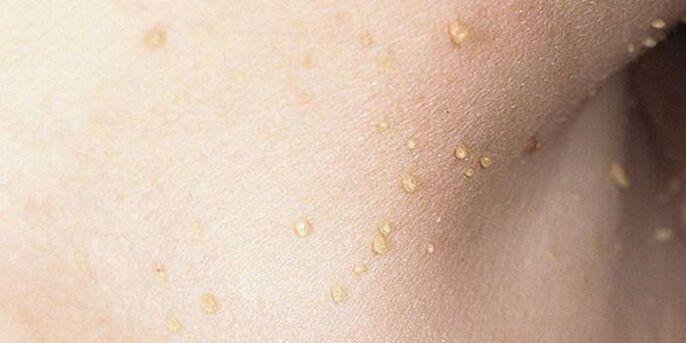
Such growths are often called warts. Their characteristic features are small size and special shape: a wide base and a sharp tip. These warts are flesh-colored or slightly pink, or appear individually or in groups. They are characterized by rapid growth: within a few days of only one growth, a whole group of them is formed. In shape, this family resembles a cauliflower bloom. Genital warts are often located on the mucous membranes: in the mouth, tongue, as well as in the genital area or near the anus.
Squamous
This form of skin growth caused by the HPV virus is one of the most common because it can have a very wide localization throughout the body. What does this type of papilloma look like? These are round or oval flat shapes, no more than 1 mm, soft and with signs of keratinization. They often appear as a group, the color is practically indistinguishable from the surrounding coating.
Such growths occur mainly in the upper part of the body: on the face (for example, on the nose or lips), on the neck. Often seen on the mucous membranes: cheeks or tongue inside the mouth. Squamous cell tumors can be diagnosed in the esophagus, larynx, as well as in the organs of the genitourinary system and even the rectum. People with such formations are advised to remove them because of the high risk of developing a malignant form.
Basal cell
These growths are often called basal cell carcinomas or old warts because they affect the skin of older people. These formations grow slowly from the basal layer of the epidermis (hence the name) or hair follicles, appearing in the form of papillae on the surface of the skin from pink to dark brown. The most common body areas for basal cell carcinomas are the armpits, back, lips, and nose. Their distinguishing feature is that they never turn into cancerous tumors, so they are considered safe.
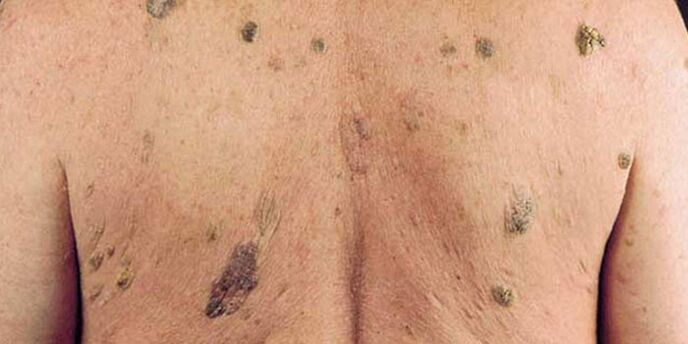
How papillomas look in intimate places
As for the formation in the genital area, pointed formations are considered. These types of papillomas are enlarged cells in the top layer of the epithelium that resemble small groups of papillae. Such increases can affect both sexes equally. It is localized in the abdomen and directly on the surface of the genitals: in men - at the head of the penis or in the lumen of the urethra, in women - in the vaginal mucosa, on the surface of the cervix and in the uterus itself.
Manifestations of changes in the genitals caused by human infection with the HPV virus require special attention from the patient. You should consult a doctor and eliminate the growths on the genitals, because the risk of infertility and oncology increases significantly with the development of such a disease into a chronic form.
Photo: how papillomas look on the body
It will be useful to look at images of what such growths look like in order to have a clear and unambiguous idea of what these formations are. Take a look at this selection of photos showing examples of different types of papillomas. With these photos, you can check the growths on yourself or your loved ones and determine in advance that these warts will be forcibly removed and prevent serious risks to your health.